N3AS Newscenter
-
post
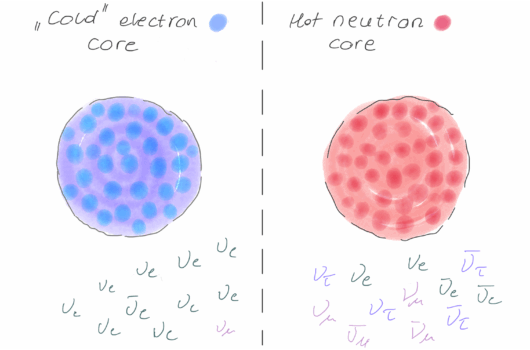
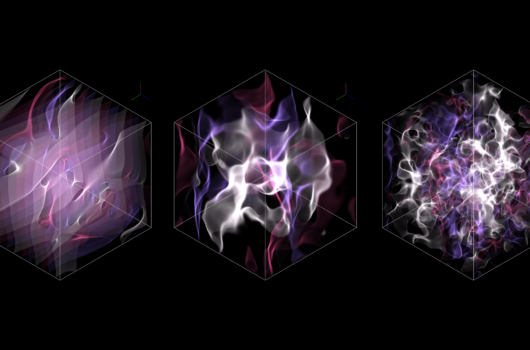
Neutrino Fast Flavor Instability in Three Dimensions
Core-collapse supernovae and neutron star mergers are profligate producers of neutrinos that would be observable at neutrino observatories on Earth if they occur sufficiently close.
-
post
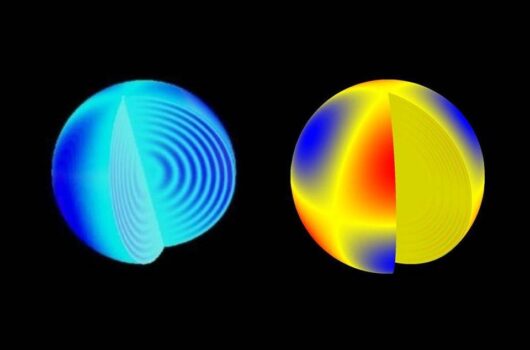
Probing Neutron Stars’ Composition with g-mode Oscillations
What can we learn from observing the “ringing” (oscillation modes) of astrophysical objects? Similar to how seismologists study the density profile and chemical constituents of the Earth using earthquakes, stellar oscillation […]
-
post
Apply to our Spring 2022 Undergraduate Research Program!
Students in the N3AS undergraduate program work with a scientific mentor to develop their research, and also have a career mentor. Students are directly supported by N3AS, and participate in […]
-
post
Where they split, they entangle: A (collective) neutrino story
Neutrinos do not experience strong or electromagnetic interactions, and are therefore by far the most feebly interacting among all the known particles in the universe. Nevertheless, there are situations where […]
-
post
Applications now open: N3AS 2022 Postdoctoral Fellows
N3AS intends to make several postdoctoral Fellow appointments for positions starting in fall 2022.